This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Fraud-proofing the consumer lending process

While the cost of fraud has risen for institutions in all industries, financial services and lending firms are experiencing the highest costs by far.
The account-based nature of the lending business, coupled with the costs of recouping losses to customer accounts and paying external labor for investigation, detection and recovery, makes fraud particularly costly for financial institutions. According to LexisNexis, every fraudulent transaction costs lenders 3.74X the lost transaction value in North America.
The implications are significant, posing substantial financial risks to lenders and emphasizing the need for enhanced fraud detection strategies to prevent potential losses.
Consumer Lending Fraud Types
Consumer lending fraud encompasses various types of illegal activities aimed at deceiving lenders and obtaining loans under false pretenses.
A few common types of consumer lending fraud encountered include:
Identity Fraud
Identity fraud is when a fraudster assumes someone else’s identity to apply for a loan. This can involve using stolen personal information, such as Social Security numbers, addresses or driver’s license details, to create fraudulent loan applications. Fraudsters attempt to secure loans they would otherwise not qualify for by impersonating a legitimate borrower, exposing lenders to non-repayment risk.
Employment Fraud
Employment fraud involves misrepresenting employment details to lenders. Fraudsters may provide false information about their employment status, job title, income, or length of employment. By inflating their job stability or income level, they deceive lenders into approving loans that the borrowers may be unable to repay.
Income Fraud
Income fraud is when individuals misrepresent their income to lenders. This can involve falsifying documents, such as pay stubs or tax returns, to inflate their earnings. Borrowers may secure more significant loan amounts or qualify for loans they would not be eligible for based on their actual income.
Straw Borrower
In a straw borrower scheme, a person with good credit and financial standing acts as a front for someone who cannot qualify for a loan due to poor credit or other reasons. The fraudster uses the straw borrower’s identity and credit history to obtain the loan, often promising them a share of the loan proceeds.
Property Value Fraud
Property value fraud involves inflating the value of a property to obtain a more significant loan amount or improve loan terms. While providing false property information or manipulating the appraisal process to deceive lenders about the true value of the collateral, fraudsters may even collude with appraisers. This type of fraud can lead to lenders approving loans that exceed the property’s actual value, increasing the risk of financial loss in case of default.
Lenders must implement robust fraud detection mechanisms and thoroughly verify borrower information to mitigate the risks associated with this growing list of fraudulent activities.
Free Checklist: 7 Tips for Preventing Document Fraud Earlier and More AccuratelyFraud Schemes and Red Flags
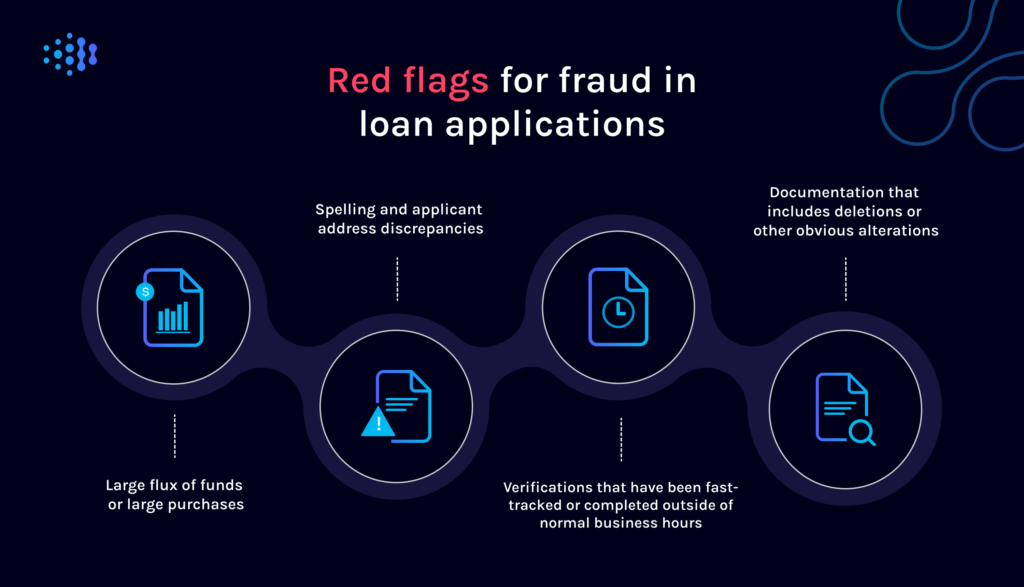
Lenders must be keen to spot common red flags indicating potential consumer lending fraud.
For example, application fraud in automotive lending is incredibly lucrative for fraudsters, as it represents the opportunity to quickly finance and secure a high-value asset, which can then be sold for cash. Some common signs of applicant fraud in automotive lending include inconsistent or suspicious documents or identification, abnormal account activity, such as sudden increases in credit usage, inflated income or false employment details.
Typically involving large sums of financial documentation and personal data, multi-family loans represent another area of opportunity for fraudsters. In this space, one scheme to be wary of is income inflation, where the fraudster may manipulate income figures. Here it’s essential to watch for inconsistencies between reported rental income and market rates and a lack of supporting documentation for rental agreements.
Another fraudulent practice to watch out for is synthetic identity fraud, where an applicant uses a stolen or fake identity using fragments of personally identifiable information. These applications might include a valid social security number associated with a confirmed address, for example, but upon closer inspection, these details won’t match the date of birth and name of a real person.
While synthetic identity fraud is often hard to detect, comparing loan application information to third-party data can reveal these sorts of discrepancies and red flags.
Download the Guide: Spotting the Fraud on Key Lending Documents: Top Signs to Look ForHow to Fraud-Proof the Lending Process
While manually detecting red flags in loan applications can be challenging and time-consuming, AI-driven automation in fraud detection can identify questionable documents more quickly and accurately than humans alone.
For example, lenders can prevent potential fraud by implementing verification procedures, including intelligent document verification, cross-referencing and thorough background checks. This helps ensure the authenticity of borrower identities, income, employment information and critical data.
By harnessing advanced data analytics techniques and machine learning algorithms, lenders can analyze extensive borrower data to detect patterns, anomalies and potential fraud indicators. By leveraging AI to identify signs of fraud quickly, lenders can quickly review suspicious documents for potential fraud and make more informed lending decisions.
Fraud Detection: A Lender’s Ultimate GuideConsumer Lending Fraud Detection Automation and AI
Standalone machine learning or AI technology can’t deliver the sort of accuracy lenders require. Ocrolus’ intelligent consumer loan automation software with human-in-the-loop powered verification enables lenders to expedite and improve the loan approval process with reliable data for lending decisions.
Our simple implementation requires zero document automation training. This enables lenders to effortlessly extract information from a full spectrum of personal loan documents and better understand a borrower’s financial health, detect potential fraud and evaluate borrower creditworthiness.
By quickly identifying document tampering with clear context, intent and advanced visualizations, we enable lenders to minimize risk and make more informed decisions that help avoid losses incurred by fraudulent borrowers.
With the cost and risk of lending fraud rising, it’s more important than ever for lenders to stay vigilant when verifying borrower documents and making consumer lending decisions.
To combat this growing problem while efficiently processing loans, lenders must leverage the right tools and technology, including intelligent document verification and advanced data analytics powered by machine learning algorithms.
By leveraging document automation and AI for reliable extraction and analysis of lending data, lenders can expedite the loan approval process, accurately identify red flags and make informed lending decisions that help prevent losses caused by fraudulent borrowers.
Are you at risk for lending fraud?
Book your demo to discover how Ocrolus empowers lenders to authenticate critical applicant details and easily identify potential signs of fraud.





